文章目录
Nginx常用的命令
启动
#配置环境变量 nginx -c nginx配置文件地址 #通过包管理器安装nginx,比如yum,apt-get service nginx start
停止
ps -ef | grep nginx #从容停止Nginx kill -QUIT 主进程号 #快速停止Nginx kill -TERM 主进程号 #强制停止Nginx pkill -9 nginx重启
修改了nginx的配置文件,需要重启下nginx服务。
nginx -s reload查看日志
nginx -s reopen – 重新打开日志平滑重启
如果更改了配置就要重启Nginx,要先关闭Nginx再打开?不是的,可以向Nginx发送信号,平滑重启!平滑重启命令:kill -HUP 主进程号或者进程号文件路径或者使用
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload注意:修改了配置文件后最好先检查一下修改过的配置文件是否正确,以免重启后Nginx出现错误影响服务器稳定运行。判断Nginx配置是否正确命令如下:
#检查指定的nginx配置文件是否正确 nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf or nginx -t #检查默认的nginx配置文件 /usr/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #-t就是检查是否配置正确
Nginx基本概念
master进程和worker进程概念
- Master进程:主要用来管理worker进程,包含:接收来自外界的信号,向各worker进程发送信号,监控worker进程的运行状态,当worker进程退出后(异常情况下),会自动重新启动新的worker进程。
- worker进程:基本的网络事件,则是放在worker进程中来处理了。多个worker进程之间是对等的,他们同等竞争来自客户端的请求,各进程互相之间是独立的。一个请求,只可能在一个worker进程中处理。worker进程的个数是可以设置的,一般我们会设置与机器cpu核数一致(更多的worker数,只会导致进程来竞争cpu资源了,从而带来不必要的上下文切换。与cpu核数一样,刚好利用好计算机的资源)

Nginx文件目录结构及原理图
下图是nginx目录下的文件:
├── client_body_temp
├── conf #配置文件目录
│ ├── fastcgi.conf
│ ├── fastcgi.conf.default
│ ├── fastcgi_params
│ ├── fastcgi_params.default
│ ├── koi-utf
│ ├── koi-win
│ ├── mime.types
│ ├── mime.types.default
│ ├── nginx.conf #主配置文件
│ ├── nginx.conf.default
│ ├── scgi_params
│ ├── scgi_params.default
│ ├── uwsgi_params
│ ├── uwsgi_params.default
│ └── win-utf
├── fastcgi_temp
├── html #初始的静态页面存放目录
│ ├── 50x.html
│ └── index.html
├── logs #日志目录
│ ├── access.log
│ ├── error.log
│ └── nginx.pid
├── proxy_temp
├── sbin #启动目录
│ └── nginx
├── scgi_temp
└── uwsgi_temp
配置文件详解
Nginx配置文件结构
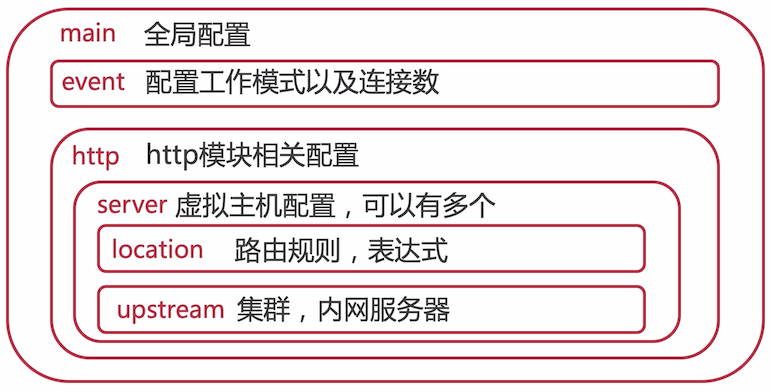
配置文件实例讲解
# 运行用户
user nobody;
#启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等
worker_processes 1;
#全局错误日志及PID文件及存放路径
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#工作模式及连接数上限
events {
#单个后台work process进程的最大并发链接数
worker_connections 1024;
}
#网页信息
http {
#设定mine类型,类型由mine。type文件定义
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#设定日志格式
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#日志文件存储路径/usr/local/...(nginx的安装目录)
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,
#对于普通应用,必须设为 on,
#如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为 off,
#以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的uptime.
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#连接超时时间
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#开启gzip压缩 如果没有开启gzip,用户访问我们的时候就是以原图来访问。
gzip on;
#小于1K的文件不适合压缩,下限是1k
gzip_min_lenth 1k;
#缓存的内存空间--4个16进制数据流
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
#http版本
gzip_http_version 1.1
#开启判断客户端和浏览器是否支持gzip
gzip_vary on;
#设定虚拟主机配置
server {
#监听80端口
listen 80;
#定义使用 访问的网址
server_name localhost;
#设置字符编码
#charset koi8-r;
#设定本虚拟主机的访问日志
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#默认请求,优先级最低的配置
location / {
#定义服务器的默认网站根目录位置 这个root目录其实就是/usr/local目录
root html;
# 匹配任何请求,因为所有请求都是以"/"开始
# 但是更长字符匹配或者正则表达式匹配会优先匹配
#定义首页索引文件的名称
index index.html index.htm;
}
#配置Nginx缓存
location ~.*\\.(jpg|png|gif)$ {
expires 30d; #缓存存放30天,然后自动清除
}
location ~.*\\.(css|js)? $ {
expires 1h; #缓存存放1小时
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#定义错误页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# 对 “/” 启用反向代理,对上面的实例
location / {
proxy_pass <http://127.0.0.1:3000>; # 设置要代理的 uri,注意最后的 /。可以是 Unix 域套接字路径,也可以是正则表达式。
proxy_redirect off; # 设置后端服务器“Location”响应头和“Refresh”响应头的替换文本
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; # 获取用户的真实 IP 地址
#后端的Web服务器可以通过 X-Forwarded-For 获取用户真实IP,多个 nginx 反代的情况下,例如 CDN。参见:<http://gong1208.iteye.com/blog/1559835> 和 <http://bbs.linuxtone.org/thread-9050-1-1.html>
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#以下是一些反向代理的配置,可选。
proxy_set_header Host $host; # 允许重新定义或者添加发往后端服务器的请求头。
client_max_body_size 10m; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数
client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数,
proxy_connect_timeout 90; #nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
proxy_send_timeout 90; #后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时)
proxy_read_timeout 90; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时)
proxy_buffer_size 4k; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
proxy_buffers 4 32k; #proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的设置
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2)
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
#设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传
}
# 本地动静分离反向代理配置
# 所有 jsp 的页面均交由tomcat或resin处理
location ~ .(jsp|jspx|do)?$ {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass <http://127.0.0.1:8080>;
}
# 所有静态文件由nginx直接读取不经过tomcat或resin
location ~ .*.(htm|html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ioc|rar|zip|txt|flv|mid|doc|ppt|pdf|xls|mp3|wma)${
root /data/www/ospring.pw/public;
expires 15d;
}
location ~ ^/(upload|html)/ {
root /data/www/ospring.pw/public/html;
expires 30d;
}
include vhosts//.conf; 分割配置文件,方便管理
}
#这里可以配置多台虚拟主机
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#配置虚拟机
#server {
# 配置监听端口,只要端口不同就是不同的虚拟主机
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
#配置访问域名
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
web服务器配置
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
location语法规则
location [=|~|~*|^~] URI { … }
规则说明
- /:默认匹配
- =:精确匹配 URI与用户URL中的URI完全一直才会显示,不是包含的关系。
- ^~:不使用正则表达式,指定字符开始的匹配
- ~:使用正则表达式,区分大小写
- ~*:使用正则表达式,不区分大小写
- !~:使用正则表达式,区分大小写,不匹配
- !~*:使用正则表达式,不区分大小写,不匹配
- URI:URL地址中从域名到参数的部分
user
user nobody:由操作系统的哪一个用户来执行指令,可以看到 worker 是 nobody 运行的,而 master 是 root,是因为 nginx 是我们主动运行的。不同用户的进程,它对于操作系统的权限是不一样的(最明显的是文件的权限)
worker_processes
配置几个 worker 服务,一般配置为 CPU 核心数,或则未核心数 减 1
error_log
配置错误的日志,文件后面的为日志级别
error_log logs/error.log;
error_log logs/error.log notice;
error_log logs/error.log info;
日志级别从低到高分别是:debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit
默认日志文件地址在我们安装的时候通过 --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/xx.log 指定了,我们不配置的话,它自己也有默认文件地址的
pid
运行时的进程 ID 文件
events
events {
# 默认使用 epoll,在 linux 下最合适的就是 epoll,其他平台上可能不一样
use epoll;
# 每个 worker 允许连接的客户端最大连接数
worker_connections 1024;
}
http
网络传输相关的模块,是一个指令块
include
include mime.types;
在 nginx.conf 同级目录下,有一个 mime.types 文件,里面也是一个指令块内容,包含了很多的 mime type
[root@bubblec conf]# cat mime.types
types {
text/html html htm shtml;
text/css css;
text/xml xml;
image/gif gif;
同理,include 就可以导入你自己的其他配置文件了,通过它来进行分类重用之类的工作
log_format
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
需要配合 access_log 使用,log_format 是日志格式的指定,记录的是 http 请求相关的日志信息
[root@bubblec conf]# cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 555 "http://192.168.56.105/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
如上所以的日志格式,就是被注释的默认格式所格式化出来的
remote_addr:ip 地址remote_user:远程用户,一般都是横杠 `` 表示无法获取time_local:访问时间request:访问方法和地址还有协议status:响应状态body_bytes_sent:响应内容的大小http_referer:用是从哪一个链接跳转过来的http_user_agent:用户代理,一般写的浏览器http_x_forwarded_for:客户端 IP,通过代理转发后的 IP
sendfile
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
文件高效传输,而 tcp_nopush 需要配合 sendfile 一起使用,含义是:当数据包内容累积到一定大小的时候才会发送,相当于是定义缓存
keepalive_timeout
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
客户端链接服务端超时的时间,http 协议里面的东西,保持长链接的空闲时间,这里单位是秒
gzip
#gzip on;
gzip 压缩开关
server
server 也就是虚拟主机
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
- listen:监听端口
- server_name:可以定义 IP 或则域名
- location:路由
- error_page:发生错误的时候,使用这里响应的状态码页面展示
pid 打开失败及解决方案
[root@bubblec nginx]# ./sbin/nginx -s reload
nginx: [error] open() "/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
其实打开这个文件失败,解决办法呢,就是先去看看这个路径的文件是否存在:
如果是
/var/run/nginx/不存在,则创建这个目录就好了mkdir /var/run/nginx/目录存在之后,再次尝试重启,报错 pid 无效
./sbin/nginx -s reload nginx: [error] invalid PID number "" in "/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid"12
解决如下
[root@bubblec nginx]# ./sbin/nginx -h nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives] Options: -?,-h : this help -v : show version and exit -V : show version and configure options then exit -t : test configuration and exit -T : test configuration, dump it and exit -q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing -s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload -p prefix : set prefix path (default: /usr/local/nginx/) -c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf) -g directives : set global directives out of configuration file查看下 nginx 的帮助,看到有一个
-c的选项,手动选择配置文件./sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf # 再次重启就可以了 ./sbin/nginx -s reloadnginx 在运行期间,这个 pid 文件丢失的话,就会出现上面的情况,执行信号指令就会报错,这个时候就只能先 kill 掉 master 进程,再手动指定下配置文件运行后,就可以了,这个 pid 文件只有在运行时才会产生
配置 Nginx 为静态资源提供服务
发布静态资源作为一个服务,供用户使用
我们可以这样做,创建一个 /usr/local/nginx/conf/my.conf 的文件,里面写指令,再在默认的配置文件里面 include 进去,分离我们自己的脚本文件的方式来组织配置
my.conf
server {
listen 90;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
}
在默认的配置文件中 include 我们的配置文件
http {
...
include my.conf;
...
重新加载 nginx: ./nginx -s reload
以上配置,我们将我们前端项目使用 nginx 部署了,这个时候可以访问 http://ip:port/ 就能访问到前端项目了
另外还可以将图片等文件配置成服务,比如 /home/foodie-shop/images 下有很多图片
location /images{
root /home/foodie-shop;
}
注:这里只是为了演示,因为这个目录在 / 下可以直接访问的 http://ip:port/images/header-bg1.jpg
上述配置后,访问 http://ip:port/images/header-bg1.jpg,它打开的文件是 /home/foodie-shop/images/header-bg1.jpg
这种方式需要注意的是:root + location + 请求的资源链接起来要是一个主机上存在的物理路径。
那么还可以使用 别名(alias) 的方式进行映射,如下所示
# 配置路由规则
location /i2 {
# 资源所在的物理路径
alias /home/foodie-shop/images;
}
访问路径变成了 http://ip:port/i2/header-bg1.jpg,也就是说 /i2 会被转成 /home/foodie-shop/images 最后拼接成完成的资源物理路径
Nginx的日志文件配置
日志文件的存储路径
控制日志的参数:
log_format:用来定义记录日志的格式(可以定义多种日志格式,取不同的名字即可)access_log:用来指定日志文件的路径及使用何种日志格式记录日志
Nginx访问日志轮询切割
为了是Nginx的日志文件存储更合理、有序,我们需要将日志文件进行分开存储,比如我们可以按时间来分开,今天的日志文件存储到一个文件中,明天的日志文件则存储到另一个新的文件中等等。这个时候,我们就会用到日志文件切割操作。
脚本实现的思想就是将正在写入的Nginx日志(access_www.log)改名为带日期的格式文件(20171011\access\www.log),然后平滑重新加载Nginx,生成新的Nginx日志。
具体切割脚本如下:
[root@bubblec logs]#cat /server/script/cut_nignx_log.sh
#!/bin/sh
Dateformat = 'date + %Y%m%d'
Basedir="/application/nginx"
Nginxlogdir="$Basedir/logs"
Logname="access_www"
[-d $Nginxlogdir ] && cd $Nginxlogdir || exit 1
[-f ${Logname}.log ] || exit 1
/bin/mv ${Logname}.log ${Dateformat}_${Logname}.log
$Basedir/sbin/nginx -s reload
#注意:脚本实现切割Nginx日志的思想为将正在写入的Nginx日志(access_www.log)改名为带日期的格式文件#(20150417_access_www.log),然后平滑重新加载Nginx,生成新的Nginx日志(access_www.log)
Nginx的缓存配置
缓存配置
当我们在浏览器中浏览某网页时,我们会把该网页上的一些信息(比如这个网页上的图片)存储到本地,当我们第二次浏览该网页的时候,这个网页上的某些信息就可以从本地加载,这样速度就会快很多。存储到本地的这些信息我们把其称为缓存。但是缓存过多的时候,缓存文件就会非常大,影响我们正常的上网活动。故而缓存需要定期清理。
进入配置文件中/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 目录
自动列目录配置
实现自动列目录需要两个条件:
- 访问的文件夹下不存在index之类的默认首页文件
- 服务器配置了自动列目录功能
在nginx.conf 配置文件中的location 字段中配置自动列目录:
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
autoindex on; #配置自动列目录,列出该目录下的所有文件
}
然后停掉nginx服务,最后重新启动nginx服务。
Nginx反向代理
注意反向代理和负载均衡的问题时,需要在nginx/nginx-1.10.1/conf/ 文件夹下新建一个配置文件,然后在重启的时候将这个配置文件加载到主配置文件中nginx.conf 中,使用/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx - c /usr/local/nginx/nginx-1.10.1/conf/fzjh.conf 命令即可实现。
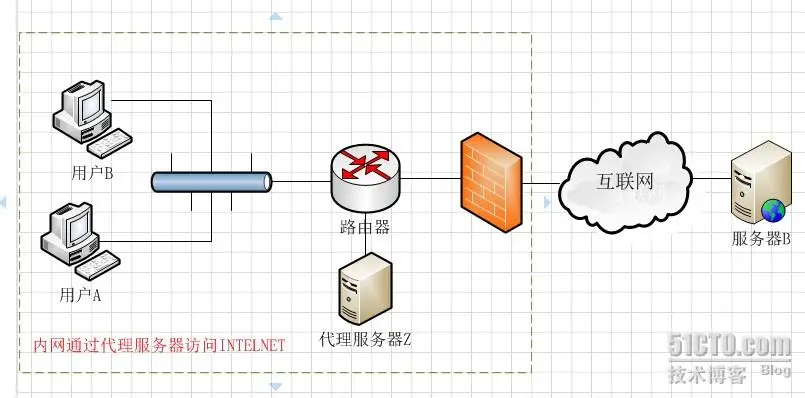
什么是正向代理?
通俗的解释:我们有时候,用自己的计算机A想访问国外的某个网站B,但是访问不了,此时,有一台中间服务器C可以访问国外的网站B,那么,我们可以用自己的电脑访问服务器C,通过C来访问B这个网站。那么这个时候,服务器C称为代理服务器,这种访问方式叫做正向代理。(例子:科学上网 :为了从外网中获取内容,代理服务器发送一个请求并指定目标(服务器B),然后代理想原始服务器B转交请求并获得的内容返回给客户端,比如你去餐厅的过程是顾客—餐厅1—餐厅2,因为顾客点的食物在餐厅1中没有,但是为了留住顾客,餐厅1到餐厅2中点餐,餐厅2将食物做好后交个餐厅1,最后由餐厅1将食物送到顾客的手里)
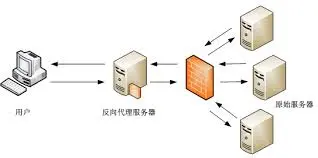
什么是反向代理?(Reverse Proxy)
通俗的解释:当我们有一个服务器集群,并且服务器集群中的每一台服务器的内容一样的时候,同样我们要直接从个人电脑访问到服务器集群中的服务器的时候无法访问,且此时第三方服务器能访问集群,这个时候,我们通过第三方服务器访问服务器集群的内容,此时我们并不知道是哪台服务器提供的内容,此时的代理称为反向代理。
(反向代理服务器对于客户端而言它就是像原始服务器,并且客户端不需要进行任何特别的设置,比如你去餐厅点餐的过程顾客—服务员—厨师。顾客在某餐厅点餐,将要吃的食物菜单交给服务员,服务员只负责将这个菜单交给厨师,自己不负责做菜,厨师将菜做好了之后叫服务员把食物送到顾客的手里)
location / {
proxy_pass <http://localhost:8000>; #需要被代理的地址
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
Nginx负载均衡
什么是负载均衡?
通俗的解释:我们可以建立很多很多服务器,这些服务器组成一个服务器集群,然后,当用户访问我们网站的时候,先访问一个中间服务器,在让这个中间服务器在服务器选择一个压力较小的服务器,然后将该访问请求引入该选择的服务器。这样,用户每次访问,都会保证服务器集群中的每个服务器的压力趋于平衡,分担了服务器压力,避免了服务器崩溃的情况。
负载均衡的实现
#负载均衡配置文件
user nobody;
events{
worker_connections 1024;
}
http{
#配置多台代理服务器地址
upstream myproject{
server 59.68.29.103; #server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server 59.68.29.108;
}
server{
listen 8080;
#在此处添加域名映射的规则
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass <http://myproject>;#
}
}
}
配置完后,重新加载Nginx配置文件
HTTP Upsteam模块
Upstream模块实现在轮询和客户端ip之间实现后端的负载均衡。常用的指令有ip_hash指令、server指令和upstream指令。
ip_hash指令
在负载均衡系统中,假如用户在某台服务器上登录,那么如果该用户第二次请求的时候,因为我们是负载均衡 系统,每次请求都会重新定位到服务器集群中的一个服务器,那么此时如果将已经登录服务器A的用户在定位到其他服务器,显然不妥。故而,我们可以采用ip_hash指令解决这个问题,如果客户端请求已经访问了服务器A并登录,那么第二次请求的时候,会将该请求通过哈希算法自动定位到该后端服务器中。
#负载均衡的服务器列表
upstream myproject{
#设置ip_hash指令:将同一个用户引向同一个服务器
ip_hash;
#服务器集群中服务器地址
server ip1:port;
server ip2:port;
}
server指令
server指令主要用于指定服务器的名称和参数。
upstream myproject{
#服务器集群中服务器地址
server ip1:port; weight=2 ;#权重越大,被访问的概率越大
server ip2:port;
}
upstream指令及相关变量
upstream指令主要是用于设置一组可以在proxy_pass和fastgi_pass指令中使用代理服务器,默认负载均衡方式为轮询。
Http转Https配置
购买域名
【腾讯云】云服务器、云数据库、COS、CDN、短信等云产品特惠热卖中
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=2446&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
【腾讯云】2核2G云服务器新老同享99元/年续费同价,8888元代金券限时抢
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=6094&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
【腾讯云】Lighthouse助力跨境电商业务扬帆出海
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=5333&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
【腾讯云】轻量新用户上云福利,2核2G4M 低至 65元/年 , 超大容量云硬盘 0.5折起!
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=1079&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
安装证书
【腾讯文档】https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/400/35244
文件说明:
- 证书文件214328891580424.pem,包含两段内容,请不要删除任何一段内容。
- 如果是证书系统创建的CSR,还包含:证书私钥文件214328891580424.key。
( 1 ) 在Nginx的安装目录下创建cert目录,并且将下载的全部文件拷贝到cert目录中。如果申请证书时是自己创建的CSR文件,请将对应的私钥文件放到cert目录下并且命名为214328891580424.key;
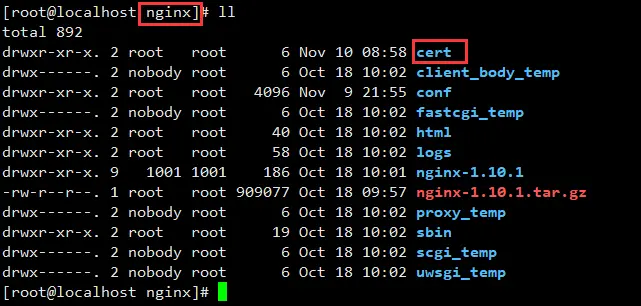
( 2 ) 打开 Nginx 安装目录下 conf 目录中的 nginx.conf 文件,找到:
# HTTPS server
# #server {
# listen 443;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl on;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1;
# ssl_ciphers ALL:!ADH:!EXPORT56:RC4+RSA:+HIGH:+MEDIUM:+LOW:+SSLv2:+EXP;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
#
#
#}
#}
( 3 ) 将其修改为 (以下属性中ssl开头的属性与证书配置有直接关系,其它属性请结合自己的实际情况复制或调整) :
server {
listen 443;
server_name localhost; #可以配置为绑定的域名,如www.michaeljian.top
ssl on;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
ssl_certificate cert/214328891580424.pem;
ssl_certificate_key cert/214328891580424.key;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
保存退出。
( 4 )重启 Nginx。
参考资料
Nginx常用的命令
启动
#配置环境变量 nginx -c nginx配置文件地址 #通过包管理器安装nginx,比如yum,apt-get service nginx start
停止
ps -ef | grep nginx #从容停止Nginx kill -QUIT 主进程号 #快速停止Nginx kill -TERM 主进程号 #强制停止Nginx pkill -9 nginx重启
修改了nginx的配置文件,需要重启下nginx服务。
nginx -s reload查看日志
nginx -s reopen – 重新打开日志平滑重启
如果更改了配置就要重启Nginx,要先关闭Nginx再打开?不是的,可以向Nginx发送信号,平滑重启!平滑重启命令:kill -HUP 主进程号或者进程号文件路径或者使用
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload注意:修改了配置文件后最好先检查一下修改过的配置文件是否正确,以免重启后Nginx出现错误影响服务器稳定运行。判断Nginx配置是否正确命令如下:
#检查指定的nginx配置文件是否正确 nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf or nginx -t #检查默认的nginx配置文件 /usr/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #-t就是检查是否配置正确
Nginx基本概念
master进程和worker进程概念
- Master进程:主要用来管理worker进程,包含:接收来自外界的信号,向各worker进程发送信号,监控worker进程的运行状态,当worker进程退出后(异常情况下),会自动重新启动新的worker进程。
- worker进程:基本的网络事件,则是放在worker进程中来处理了。多个worker进程之间是对等的,他们同等竞争来自客户端的请求,各进程互相之间是独立的。一个请求,只可能在一个worker进程中处理。worker进程的个数是可以设置的,一般我们会设置与机器cpu核数一致(更多的worker数,只会导致进程来竞争cpu资源了,从而带来不必要的上下文切换。与cpu核数一样,刚好利用好计算机的资源)

Nginx文件目录结构及原理图
下图是nginx目录下的文件:
├── client_body_temp
├── conf #配置文件目录
│ ├── fastcgi.conf
│ ├── fastcgi.conf.default
│ ├── fastcgi_params
│ ├── fastcgi_params.default
│ ├── koi-utf
│ ├── koi-win
│ ├── mime.types
│ ├── mime.types.default
│ ├── nginx.conf #主配置文件
│ ├── nginx.conf.default
│ ├── scgi_params
│ ├── scgi_params.default
│ ├── uwsgi_params
│ ├── uwsgi_params.default
│ └── win-utf
├── fastcgi_temp
├── html #初始的静态页面存放目录
│ ├── 50x.html
│ └── index.html
├── logs #日志目录
│ ├── access.log
│ ├── error.log
│ └── nginx.pid
├── proxy_temp
├── sbin #启动目录
│ └── nginx
├── scgi_temp
└── uwsgi_temp
配置文件详解
Nginx配置文件结构

配置文件实例讲解
# 运行用户
user nobody;
#启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等
worker_processes 1;
#全局错误日志及PID文件及存放路径
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#工作模式及连接数上限
events {
#单个后台work process进程的最大并发链接数
worker_connections 1024;
}
#网页信息
http {
#设定mine类型,类型由mine。type文件定义
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#设定日志格式
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#日志文件存储路径/usr/local/...(nginx的安装目录)
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,
#对于普通应用,必须设为 on,
#如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为 off,
#以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的uptime.
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#连接超时时间
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#开启gzip压缩 如果没有开启gzip,用户访问我们的时候就是以原图来访问。
gzip on;
#小于1K的文件不适合压缩,下限是1k
gzip_min_lenth 1k;
#缓存的内存空间--4个16进制数据流
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
#http版本
gzip_http_version 1.1
#开启判断客户端和浏览器是否支持gzip
gzip_vary on;
#设定虚拟主机配置
server {
#监听80端口
listen 80;
#定义使用 访问的网址
server_name localhost;
#设置字符编码
#charset koi8-r;
#设定本虚拟主机的访问日志
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#默认请求,优先级最低的配置
location / {
#定义服务器的默认网站根目录位置 这个root目录其实就是/usr/local目录
root html;
# 匹配任何请求,因为所有请求都是以"/"开始
# 但是更长字符匹配或者正则表达式匹配会优先匹配
#定义首页索引文件的名称
index index.html index.htm;
}
#配置Nginx缓存
location ~.*\.(jpg|png|gif)$ {
expires 30d; #缓存存放30天,然后自动清除
}
location ~.*\.(css|js)? $ {
expires 1h; #缓存存放1小时
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#定义错误页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# 对 “/” 启用反向代理,对上面的实例
location / {
proxy_pass <http://127.0.0.1:3000>; # 设置要代理的 uri,注意最后的 /。可以是 Unix 域套接字路径,也可以是正则表达式。
proxy_redirect off; # 设置后端服务器“Location”响应头和“Refresh”响应头的替换文本
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; # 获取用户的真实 IP 地址
#后端的Web服务器可以通过 X-Forwarded-For 获取用户真实IP,多个 nginx 反代的情况下,例如 CDN。参见:<http://gong1208.iteye.com/blog/1559835> 和 <http://bbs.linuxtone.org/thread-9050-1-1.html>
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#以下是一些反向代理的配置,可选。
proxy_set_header Host $host; # 允许重新定义或者添加发往后端服务器的请求头。
client_max_body_size 10m; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数
client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数,
proxy_connect_timeout 90; #nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
proxy_send_timeout 90; #后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时)
proxy_read_timeout 90; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时)
proxy_buffer_size 4k; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
proxy_buffers 4 32k; #proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的设置
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2)
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
#设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传
}
# 本地动静分离反向代理配置
# 所有 jsp 的页面均交由tomcat或resin处理
location ~ .(jsp|jspx|do)?$ {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass <http://127.0.0.1:8080>;
}
# 所有静态文件由nginx直接读取不经过tomcat或resin
location ~ .*.(htm|html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ioc|rar|zip|txt|flv|mid|doc|ppt|pdf|xls|mp3|wma)${
root /data/www/ospring.pw/public;
expires 15d;
}
location ~ ^/(upload|html)/ {
root /data/www/ospring.pw/public/html;
expires 30d;
}
include vhosts//.conf; 分割配置文件,方便管理
}
#这里可以配置多台虚拟主机
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#配置虚拟机
#server {
# 配置监听端口,只要端口不同就是不同的虚拟主机
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
#配置访问域名
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
web服务器配置
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
location语法规则
location [=|~|~*|^~] URI { … }
规则说明
- /:默认匹配
- =:精确匹配 URI与用户URL中的URI完全一直才会显示,不是包含的关系。
- ^~:不使用正则表达式,指定字符开始的匹配
- ~:使用正则表达式,区分大小写
- ~*:使用正则表达式,不区分大小写
- !~:使用正则表达式,区分大小写,不匹配
- !~*:使用正则表达式,不区分大小写,不匹配
- URI:URL地址中从域名到参数的部分
user
user nobody:由操作系统的哪一个用户来执行指令,可以看到 worker 是 nobody 运行的,而 master 是 root,是因为 nginx 是我们主动运行的。不同用户的进程,它对于操作系统的权限是不一样的(最明显的是文件的权限)
worker_processes
配置几个 worker 服务,一般配置为 CPU 核心数,或则未核心数 减 1
error_log
配置错误的日志,文件后面的为日志级别
error_log logs/error.log;
error_log logs/error.log notice;
error_log logs/error.log info;
日志级别从低到高分别是:debug、info、notice、warn、error、crit
默认日志文件地址在我们安装的时候通过 --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/xx.log 指定了,我们不配置的话,它自己也有默认文件地址的
pid
运行时的进程 ID 文件
events
events {
# 默认使用 epoll,在 linux 下最合适的就是 epoll,其他平台上可能不一样
use epoll;
# 每个 worker 允许连接的客户端最大连接数
worker_connections 1024;
}
http
网络传输相关的模块,是一个指令块
include
include mime.types;
在 nginx.conf 同级目录下,有一个 mime.types 文件,里面也是一个指令块内容,包含了很多的 mime type
[root@bubblec conf]# cat mime.types
types {
text/html html htm shtml;
text/css css;
text/xml xml;
image/gif gif;
同理,include 就可以导入你自己的其他配置文件了,通过它来进行分类重用之类的工作
log_format
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
需要配合 access_log 使用,log_format 是日志格式的指定,记录的是 http 请求相关的日志信息
[root@bubblec conf]# cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
192.168.56.1 - - [04/Apr/2021:16:32:44 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 555 "http://192.168.56.105/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_2_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36"
如上所以的日志格式,就是被注释的默认格式所格式化出来的
remote_addr:ip 地址remote_user:远程用户,一般都是横杠 `` 表示无法获取time_local:访问时间request:访问方法和地址还有协议status:响应状态body_bytes_sent:响应内容的大小http_referer:用是从哪一个链接跳转过来的http_user_agent:用户代理,一般写的浏览器http_x_forwarded_for:客户端 IP,通过代理转发后的 IP
sendfile
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
文件高效传输,而 tcp_nopush 需要配合 sendfile 一起使用,含义是:当数据包内容累积到一定大小的时候才会发送,相当于是定义缓存
keepalive_timeout
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
客户端链接服务端超时的时间,http 协议里面的东西,保持长链接的空闲时间,这里单位是秒
gzip
#gzip on;
gzip 压缩开关
server
server 也就是虚拟主机
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ .php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ .php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
- listen:监听端口
- server_name:可以定义 IP 或则域名
- location:路由
- error_page:发生错误的时候,使用这里响应的状态码页面展示
pid 打开失败及解决方案
[root@bubblec nginx]# ./sbin/nginx -s reload
nginx: [error] open() "/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid" failed (2: No such file or directory)
其实打开这个文件失败,解决办法呢,就是先去看看这个路径的文件是否存在:
如果是
/var/run/nginx/不存在,则创建这个目录就好了mkdir /var/run/nginx/目录存在之后,再次尝试重启,报错 pid 无效
./sbin/nginx -s reload nginx: [error] invalid PID number "" in "/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid"12
解决如下
[root@bubblec nginx]# ./sbin/nginx -h nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives] Options: -?,-h : this help -v : show version and exit -V : show version and configure options then exit -t : test configuration and exit -T : test configuration, dump it and exit -q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing -s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload -p prefix : set prefix path (default: /usr/local/nginx/) -c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf) -g directives : set global directives out of configuration file查看下 nginx 的帮助,看到有一个
-c的选项,手动选择配置文件./sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf # 再次重启就可以了 ./sbin/nginx -s reloadnginx 在运行期间,这个 pid 文件丢失的话,就会出现上面的情况,执行信号指令就会报错,这个时候就只能先 kill 掉 master 进程,再手动指定下配置文件运行后,就可以了,这个 pid 文件只有在运行时才会产生
配置 Nginx 为静态资源提供服务
发布静态资源作为一个服务,供用户使用
我们可以这样做,创建一个 /usr/local/nginx/conf/my.conf 的文件,里面写指令,再在默认的配置文件里面 include 进去,分离我们自己的脚本文件的方式来组织配置
my.conf
server {
listen 90;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /home/foodie-shop/;
index index.html;
}
}
在默认的配置文件中 include 我们的配置文件
http {
...
include my.conf;
...
重新加载 nginx: ./nginx -s reload
以上配置,我们将我们前端项目使用 nginx 部署了,这个时候可以访问 http://ip:port/ 就能访问到前端项目了
另外还可以将图片等文件配置成服务,比如 /home/foodie-shop/images 下有很多图片
location /images{
root /home/foodie-shop;
}
注:这里只是为了演示,因为这个目录在 / 下可以直接访问的 http://ip:port/images/header-bg1.jpg
上述配置后,访问 http://ip:port/images/header-bg1.jpg,它打开的文件是 /home/foodie-shop/images/header-bg1.jpg
这种方式需要注意的是:root + location + 请求的资源链接起来要是一个主机上存在的物理路径。
那么还可以使用 别名(alias) 的方式进行映射,如下所示
# 配置路由规则
location /i2 {
# 资源所在的物理路径
alias /home/foodie-shop/images;
}
访问路径变成了 http://ip:port/i2/header-bg1.jpg,也就是说 /i2 会被转成 /home/foodie-shop/images 最后拼接成完成的资源物理路径
Nginx的日志文件配置
日志文件的存储路径
控制日志的参数:
log_format:用来定义记录日志的格式(可以定义多种日志格式,取不同的名字即可)access_log:用来指定日志文件的路径及使用何种日志格式记录日志
Nginx访问日志轮询切割
为了是Nginx的日志文件存储更合理、有序,我们需要将日志文件进行分开存储,比如我们可以按时间来分开,今天的日志文件存储到一个文件中,明天的日志文件则存储到另一个新的文件中等等。这个时候,我们就会用到日志文件切割操作。
脚本实现的思想就是将正在写入的Nginx日志(access_www.log)改名为带日期的格式文件(20171011accesswww.log),然后平滑重新加载Nginx,生成新的Nginx日志。
具体切割脚本如下:
[root@bubblec logs]#cat /server/script/cut_nignx_log.sh
#!/bin/sh
Dateformat = 'date + %Y%m%d'
Basedir="/application/nginx"
Nginxlogdir="$Basedir/logs"
Logname="access_www"
[-d $Nginxlogdir ] && cd $Nginxlogdir || exit 1
[-f ${Logname}.log ] || exit 1
/bin/mv ${Logname}.log ${Dateformat}_${Logname}.log
$Basedir/sbin/nginx -s reload
#注意:脚本实现切割Nginx日志的思想为将正在写入的Nginx日志(access_www.log)改名为带日期的格式文件#(20150417_access_www.log),然后平滑重新加载Nginx,生成新的Nginx日志(access_www.log)
Nginx的缓存配置
缓存配置
当我们在浏览器中浏览某网页时,我们会把该网页上的一些信息(比如这个网页上的图片)存储到本地,当我们第二次浏览该网页的时候,这个网页上的某些信息就可以从本地加载,这样速度就会快很多。存储到本地的这些信息我们把其称为缓存。但是缓存过多的时候,缓存文件就会非常大,影响我们正常的上网活动。故而缓存需要定期清理。
进入配置文件中/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 目录
自动列目录配置
实现自动列目录需要两个条件:
- 访问的文件夹下不存在index之类的默认首页文件
- 服务器配置了自动列目录功能
在nginx.conf 配置文件中的location 字段中配置自动列目录:
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
autoindex on; #配置自动列目录,列出该目录下的所有文件
}
然后停掉nginx服务,最后重新启动nginx服务。
Nginx反向代理
注意反向代理和负载均衡的问题时,需要在nginx/nginx-1.10.1/conf/ 文件夹下新建一个配置文件,然后在重启的时候将这个配置文件加载到主配置文件中nginx.conf 中,使用/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx - c /usr/local/nginx/nginx-1.10.1/conf/fzjh.conf 命令即可实现。
什么是正向代理?
通俗的解释:我们有时候,用自己的计算机A想访问国外的某个网站B,但是访问不了,此时,有一台中间服务器C可以访问国外的网站B,那么,我们可以用自己的电脑访问服务器C,通过C来访问B这个网站。那么这个时候,服务器C称为代理服务器,这种访问方式叫做正向代理。(例子:科学上网 :为了从外网中获取内容,代理服务器发送一个请求并指定目标(服务器B),然后代理想原始服务器B转交请求并获得的内容返回给客户端,比如你去餐厅的过程是顾客—餐厅1—餐厅2,因为顾客点的食物在餐厅1中没有,但是为了留住顾客,餐厅1到餐厅2中点餐,餐厅2将食物做好后交个餐厅1,最后由餐厅1将食物送到顾客的手里)

什么是反向代理?(Reverse Proxy)
通俗的解释:当我们有一个服务器集群,并且服务器集群中的每一台服务器的内容一样的时候,同样我们要直接从个人电脑访问到服务器集群中的服务器的时候无法访问,且此时第三方服务器能访问集群,这个时候,我们通过第三方服务器访问服务器集群的内容,此时我们并不知道是哪台服务器提供的内容,此时的代理称为反向代理。
(反向代理服务器对于客户端而言它就是像原始服务器,并且客户端不需要进行任何特别的设置,比如你去餐厅点餐的过程顾客—服务员—厨师。顾客在某餐厅点餐,将要吃的食物菜单交给服务员,服务员只负责将这个菜单交给厨师,自己不负责做菜,厨师将菜做好了之后叫服务员把食物送到顾客的手里)

location / {
proxy_pass <http://localhost:8000>; #需要被代理的地址
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
Nginx负载均衡
什么是负载均衡?
通俗的解释:我们可以建立很多很多服务器,这些服务器组成一个服务器集群,然后,当用户访问我们网站的时候,先访问一个中间服务器,在让这个中间服务器在服务器选择一个压力较小的服务器,然后将该访问请求引入该选择的服务器。这样,用户每次访问,都会保证服务器集群中的每个服务器的压力趋于平衡,分担了服务器压力,避免了服务器崩溃的情况。
负载均衡的实现
#负载均衡配置文件
user nobody;
events{
worker_connections 1024;
}
http{
#配置多台代理服务器地址
upstream myproject{
server 59.68.29.103; #server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server 59.68.29.108;
}
server{
listen 8080;
#在此处添加域名映射的规则
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass <http://myproject>;#
}
}
}
配置完后,重新加载Nginx配置文件
HTTP Upsteam模块
Upstream模块实现在轮询和客户端ip之间实现后端的负载均衡。常用的指令有ip_hash指令、server指令和upstream指令。
ip_hash指令
在负载均衡系统中,假如用户在某台服务器上登录,那么如果该用户第二次请求的时候,因为我们是负载均衡 系统,每次请求都会重新定位到服务器集群中的一个服务器,那么此时如果将已经登录服务器A的用户在定位到其他服务器,显然不妥。故而,我们可以采用ip_hash指令解决这个问题,如果客户端请求已经访问了服务器A并登录,那么第二次请求的时候,会将该请求通过哈希算法自动定位到该后端服务器中。
#负载均衡的服务器列表
upstream myproject{
#设置ip_hash指令:将同一个用户引向同一个服务器
ip_hash;
#服务器集群中服务器地址
server ip1:port;
server ip2:port;
}
server指令
server指令主要用于指定服务器的名称和参数。
upstream myproject{
#服务器集群中服务器地址
server ip1:port; weight=2 ;#权重越大,被访问的概率越大
server ip2:port;
}
upstream指令及相关变量
upstream指令主要是用于设置一组可以在proxy_pass和fastgi_pass指令中使用代理服务器,默认负载均衡方式为轮询。
Http转Https配置
购买域名
【腾讯云】云服务器、云数据库、COS、CDN、短信等云产品特惠热卖中
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=2446&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
【腾讯云】2核2G云服务器新老同享99元/年续费同价,8888元代金券限时抢
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=6094&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
【腾讯云】Lighthouse助力跨境电商业务扬帆出海
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=5333&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
【腾讯云】轻量新用户上云福利,2核2G4M 低至 65元/年 , 超大容量云硬盘 0.5折起!
https://cloud.tencent.com/act/cps/redirect?redirect=1079&cps_key=bd44b1f4be139d78245e2a532dd5d073&from=console
安装证书
【腾讯文档】https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/400/35244
文件说明:
- 证书文件214328891580424.pem,包含两段内容,请不要删除任何一段内容。
- 如果是证书系统创建的CSR,还包含:证书私钥文件214328891580424.key。
( 1 ) 在Nginx的安装目录下创建cert目录,并且将下载的全部文件拷贝到cert目录中。如果申请证书时是自己创建的CSR文件,请将对应的私钥文件放到cert目录下并且命名为214328891580424.key;

( 2 ) 打开 Nginx 安装目录下 conf 目录中的 nginx.conf 文件,找到:
# HTTPS server
# #server {
# listen 443;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl on;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1;
# ssl_ciphers ALL:!ADH:!EXPORT56:RC4+RSA:+HIGH:+MEDIUM:+LOW:+SSLv2:+EXP;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
#
#
#}
#}
( 3 ) 将其修改为 (以下属性中ssl开头的属性与证书配置有直接关系,其它属性请结合自己的实际情况复制或调整) :
server {
listen 443;
server_name localhost; #可以配置为绑定的域名,如www.michaeljian.top
ssl on;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
ssl_certificate cert/214328891580424.pem;
ssl_certificate_key cert/214328891580424.key;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE:ECDH:AES:HIGH:!NULL:!aNULL:!MD5:!ADH:!RC4;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
保存退出。
( 4 )重启 Nginx。
参考资料
- 本文作者:
- 原文链接:
- 版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用进行许可。转载请署名作者且注明文章出处。
 Java技术债务
Java技术债务


